

As noted above,, leaving Mac owners who solely rely on XProtect and other features susceptible to attack.

A component of strong antivirus protection is a current and comprehensive database of virus definitions.
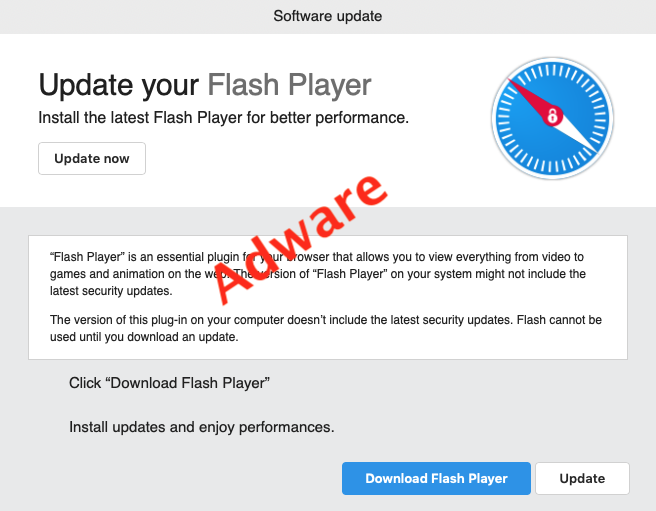
HOW CAN I TELL IF MY MAC IS INFECTED FREE
Per Apple, “We review all apps and app updates submitted to the App Store in an effort to determine whether they are reliable, perform as expected, respect user privacy, and are free of objectionable content.” While not strictly a review for malware, security matters are considered in the process. Similarly, all apps that wish to be sold on the Apple App Store must go through Apple’s App Review. Additionally, if a previously approved app is later to found to be malicious, Apple can revoke its Notarization and prevent it from running. That ticket is recognized in another part of the MacOS, Gatekeeper, which verifies the ticket and allows the app to launch. When this review turns up no instances of malware, Apple issues a Notarization ticket. Notarization, Gatekeeper, and the App Review Process: Another way Apple keeps its users safe across MacOS and iOS devices is its Notarization Apps built to run on Apple devices go through an initial review before they can be distributed and sold outside of Apple’s App Store.According to Apple, MRT removes malware upon receiving updated information, and it continues to check for infections on restart and login. Similar to XProtect, it relies on a set of constantly updated definitions that help identify potential malware. Malware Removal Tool: To further keep Apple users protected, the Malware Removal Tool (MRT) scans Macs to spot and catch any malware that may have slipped past XProtect.From there, suspicious files are quarantined by limiting their access to the Mac’s operating system and other key functions. Functionally, it works the same as any other antivirus, where it scans files and apps for malware by referencing a database of known threats that Apple maintains and updates regularly.
HOW CAN I TELL IF MY MAC IS INFECTED SOFTWARE
Similarly, if you see spikes in your data usage, that could be a sign of a hack as well. A hacker may have hijacked your computer to send messages or to spread malware to your contacts. If you find apps you haven’t downloaded, along with messages and emails that you didn’t send, that’s a red flag. Aside from sapping performance, malware and mining apps can cause your computer to run hot or even overheat.
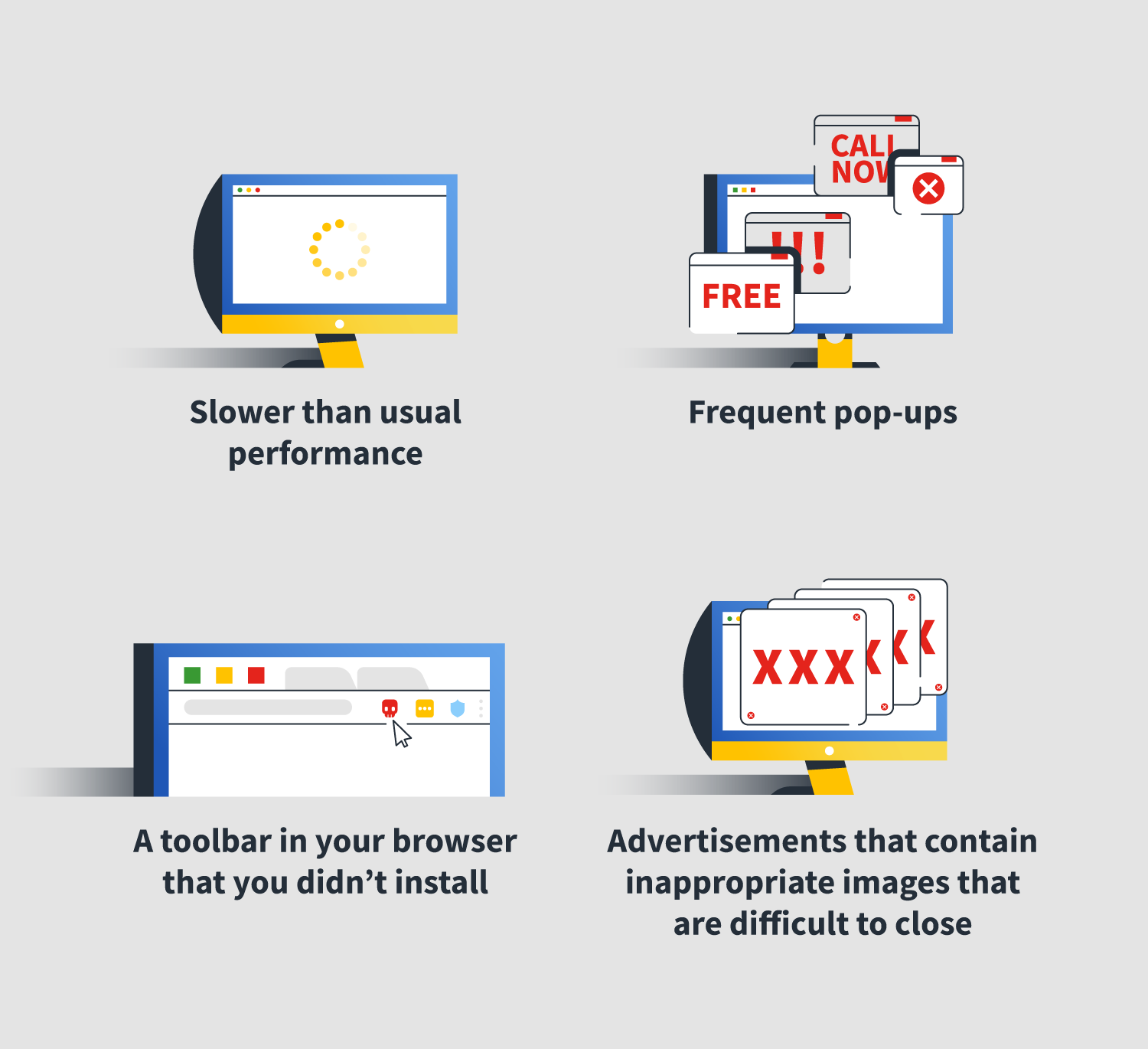
Like the performance issues above, malware or mining apps running in the background can burn extra computing power (and data). Your computer feels like it’s running hot Is your device operating more slowly, are web pages and apps harder to load, or does your battery never seem to keep a charge? These are all signs that you could have malware running in the background, zapping your device’s resources. Some possible signs of hacking software on your Mac include: Performance issues While cryptomining is not illegal, “ cryptojacking” a device without the owner’s consent is most certainly illegal. From there, it harnesses the device’s computing power to “mine” cryptocurrencies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
